Prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities
Introduction to Prompt Engineering Debugging
Prompt debugging is the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues in LLM prompts to ensure optimal AI responses. This critical practice has become essential as organizations increasingly rely on large language models for various applications. Without proper debugging tools, prompt engineers face significant challenges in tracking changes, evaluating performance, and ensuring consistent outputs.
The challenges of prompt engineering without specialized tools are numerous. Engineers struggle with version control, lack objective performance metrics, and find it difficult to pinpoint exactly why certain prompts fail. This leads to inefficient trial-and-error approaches, inconsistent results, and ultimately, less reliable AI applications.
My Take: Debugging capabilities represent the maturation of prompt engineering as a discipline. As LLMs become central to business operations, the need for systematic, data-driven approaches to prompt optimization has transformed from a nice-to-have into a mission-critical requirement. Market consensus indicates that organizations without structured debugging processes face significantly longer development cycles and higher rates of prompt failure.
Key Capabilities of Prompt Debugging Tools
Modern prompt debugging platforms offer several essential capabilities:
- Prompt versioning and history tracking: Tools maintain comprehensive records of prompt iterations, allowing engineers to revert to previous versions when needed.
- Side-by-side comparison: Visual interfaces that display outputs from different prompt variations simultaneously, enabling direct assessment of performance differences.
- Real-time inspection: Detailed visibility into inputs, outputs, and intermediate steps of LLM processing for thorough analysis.
- Automated evaluation metrics: Quantitative measurements like semantic similarity and correctness scores that objectively assess prompt effectiveness.
- Error logging and failure analysis: Systematic recording of failures with contextual information to identify patterns and root causes.
- A/B testing frameworks: Structured environments for comparing prompt performance in production scenarios.
- Observability features: Monitoring of token usage, latency, and cost per LLM call to optimize resource utilization.
My Take: The most sophisticated prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities now bundle version control, evaluation metrics, and observability into one workflow, allowing teams to standardize how they test, compare, and refine prompts instead of relying on ad-hoc scripts and manual checks.
How Prompt Debugging Tools Enhance Development Workflows
Prompt debugging tools significantly accelerate the development process by enabling rapid iteration and optimization. By providing structured workflows for testing and evaluation, these platforms help engineers quickly identify and address issues in their prompts. This systematic approach leads to more reliable and consistent AI applications.
One of the most valuable benefits is the reduction of hallucinations and undesirable outputs. Through careful analysis and testing, engineers can refine prompts to minimize inaccuracies and ensure responses align with intended purposes. Additionally, these tools facilitate collaborative prompt development, allowing teams to work together effectively on complex AI applications.
My Take: When prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities are integrated into day-to-day development, teams tend to move from manual trial-and-error to repeatable experiments, which shortens iteration cycles and makes it easier to institutionalize best practices across projects.
Who Benefits Most from Prompt Debugging Capabilities?
Several key roles derive significant value from prompt debugging tools:
- Prompt engineers and AI/ML developers: Those directly responsible for creating and optimizing LLM interactions.
- Data scientists: Professionals analyzing and improving model performance through prompt refinement.
- Product managers: Team members overseeing AI-powered features who need visibility into prompt performance.
- Researchers and innovators: Those exploring new applications and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with LLMs.
- Enterprise teams: Organizations requiring quality control and governance over AI-driven products.
My Take: The impact of prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities compounds at scale: individual practitioners gain faster feedback, while larger organizations get consistent governance, shared artifacts, and clearer accountability around prompt behavior.
Comparing Leading Prompt Engineering Debugging Tools
The market offers several specialized platforms with distinct approaches to prompt debugging:
Comparison of Prompt Engineering Tools with Debugging Capabilities
| Tool | Primary Focus | Debugging Strength | Starting Price | Free Plan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Braintrust | Prompt evaluation and versioning | Detailed metrics and full prompt history tracking | $249 / month | Yes |
| Humanloop | Prompt experimentation | A/B testing and production comparisons | $100 / month | Yes |
| Weights & Biases (W&B Prompts) | MLOps-integrated prompt tracking | Prompt performance alongside model metrics | $35 / month | Yes |
| LangSmith | LLM observability | Tracing and debugging multi-step prompt chains | $39 / month | Yes |
| LlamaIndex | Data-centric prompt workflows | Analysis of prompt–data interactions | $5 / month | Yes |
| OpenAI Playground | Interactive prompt testing | Quick iteration and basic inspection | Free | Yes |
Braintrust
Braintrust focuses on comprehensive evaluation and versioning capabilities. The platform excels in providing detailed performance metrics and maintaining a complete history of prompt iterations. Its strengths lie in facilitating systematic prompt improvement through data-driven insights and robust version control.
Humanloop
Humanloop emphasizes experimentation and A/B testing frameworks. The platform provides powerful tools for comparing different prompt variations in production environments. Its approach centers on helping teams identify the most effective prompts through structured testing and evaluation.
Weights & Biases (W&B Prompts)
W&B Prompts integrates prompt management into a broader MLOps ecosystem. This integration allows teams to track prompt performance alongside model metrics, providing a holistic view of AI application performance. The platform offers robust visualization tools for analyzing prompt effectiveness.
LangChain (LangSmith)
LangSmith provides observability for complex LLM applications, particularly those built with the LangChain framework. The platform excels at tracing and debugging multi-step LLM workflows, offering insights into each component of the chain. Its trace analysis capabilities help identify bottlenecks and failure points in sophisticated applications.
LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex takes a data-centric approach to prompt debugging, focusing on the interaction between prompts and the data they reference. The platform provides tools for analyzing how prompts retrieve and utilize information, helping engineers optimize for accuracy and relevance in data-intensive applications.
OpenAI Playground
OpenAI Playground offers basic interactive testing capabilities directly integrated with OpenAI’s models. While less feature-rich than dedicated platforms, it provides a simple environment for quick prompt iteration and testing. The playground is particularly useful for initial prompt development and basic refinement.
My Take: The market has segmented into specialized prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities that map to different maturity levels: some emphasize quick experimentation, others deep observability or tight MLOps integration, so alignment with existing workflows usually matters more than raw feature count.
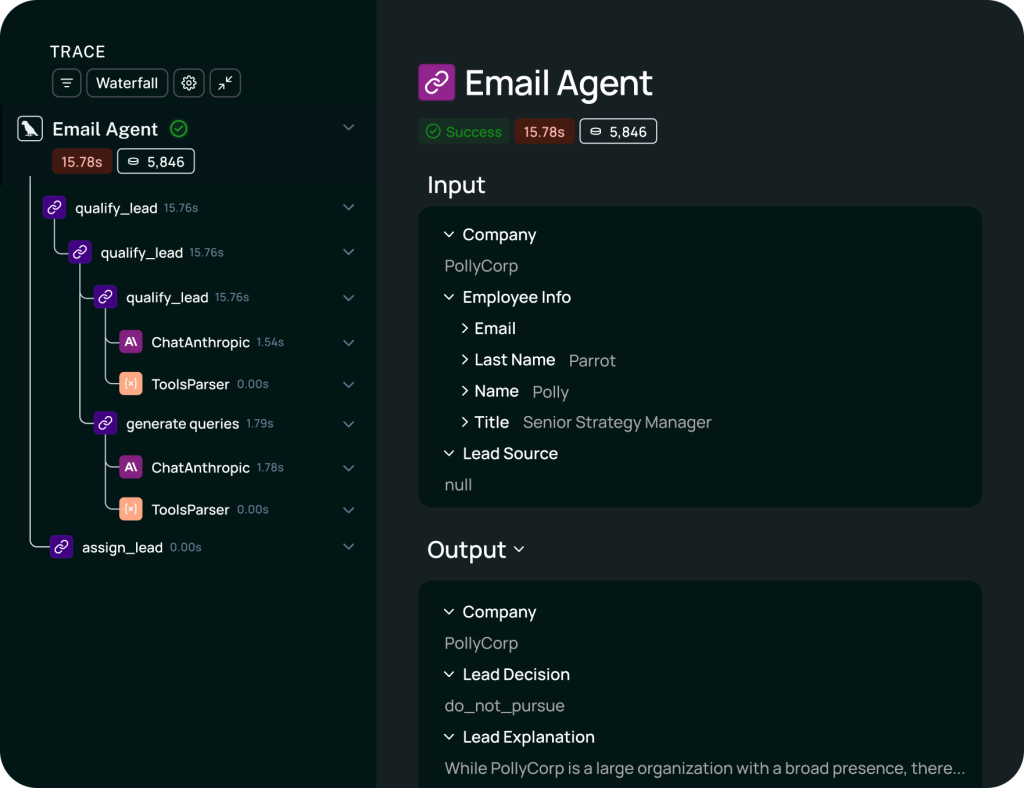
How I’d Use It: The “X-Ray Vision” Workflow
If I were building a customer support chatbot and it started making up fake refund policies (Hallucinations), I wouldn’t just randomly rewrite the prompt. I would use LangSmith or Braintrust to see “inside” the brain of the AI.
Here is my debugging routine:
- Trace Analysis: Instead of guessing, I would open the “Trace View” to pinpoint exactly which step in the chain caused the error.
- Regression Testing: Before pushing a fix, I would run the new prompt against a “Golden Dataset” (a list of 50 tricky questions) to ensure I didn’t break other features while fixing this one.
- Token Optimization: I would check the “Token Count” column to see if I can shorten the prompt to save API costs without losing quality.
Bottom line: This turns prompt engineering from a game of “blind guessing” into actual, data-driven engineering.
Limitations and Considerations for Adoption
Despite their benefits, prompt debugging tools come with several considerations. Integration complexity with existing tech stacks can be significant, requiring careful planning and potentially substantial development resources. Many platforms also present a learning curve for new users, necessitating training and adaptation periods.
Scalability concerns emerge for high-volume use cases, as some tools may struggle with the performance demands of large-scale production environments. Additionally, organizations should consider the risk of vendor lock-in and API dependencies, which can limit flexibility and increase costs over time.
My Take: From an adoption standpoint, prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities tend to deliver the best results when introduced early in a project and integrated incrementally, reducing migration risk and giving teams time to standardize on shared evaluation and logging practices.
Future Trends in Prompt Debugging
The prompt debugging landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Emerging trends include advanced AI-assisted debugging suggestions, which leverage meta-LLMs to identify and resolve issues in prompts automatically. Enhanced visual interfaces for complex prompt flows are also gaining prominence, making it easier to understand and optimize multi-step interactions.
Another significant trend is broader multi-modal prompt support, extending debugging capabilities beyond text to include images, audio, and other input types. Finally, closer integration with IDEs and developer environments is streamlining the prompt engineering workflow, embedding debugging tools directly into familiar development processes.
My Take: As vendors compete, prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities are likely to converge on AI-assisted suggestions, richer visual traces, and native IDE plug-ins, shifting debugging from a reactive task to a proactive, guided optimization loop.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Debugging in Prompt Engineering
Prompt debugging has emerged as a critical discipline for organizations leveraging LLMs in production environments. The tools and methodologies in this space enable systematic improvement of AI applications, reducing errors and enhancing reliability. As LLMs continue to proliferate across industries, robust debugging capabilities will remain essential for ensuring these powerful technologies deliver consistent, accurate, and valuable results.
Pricing Plans
Below is the current pricing overview for the tools mentioned above:
- Braintrust: $249/mo, Free Plan Available
- Humanloop: $100/mo, Free Plan Available
- Weights & Biases (W&B Prompts): $35/mo, Free Plan Available
- LangSmith: $39/mo, Free Plan Available
- LlamaIndex: $5/mo, Free Plan Available
- OpenAI Playground: Free Plan Available
Value for Money
When evaluating value relative to investment, LlamaIndex stands out for budget-conscious teams seeking entry-level debugging capabilities. Its low entry point makes it accessible for startups and individual developers while still providing essential functionality. However, the platform’s specialized focus on data retrieval means it may not satisfy all debugging requirements.
For mid-range options, LangSmith and W&B Prompts deliver strong value propositions for different use cases. LangSmith offers exceptional value for teams already using LangChain, providing specialized observability for complex chains at a reasonable price point. W&B Prompts, while slightly less expensive, delivers broader MLOps integration that proves valuable for organizations with more comprehensive machine learning pipelines.
At the premium end, Braintrust and Humanloop justify their higher price points through enterprise-grade capabilities and comprehensive feature sets. These platforms typically deliver the strongest ROI for larger organizations where prompt reliability directly impacts business outcomes. The extensive evaluation frameworks and collaboration features these tools provide can significantly reduce development time and improve prompt quality, often justifying the investment for teams working on business-critical AI applications.

Editor’s Summary
Prompt engineering tools with debugging capabilities now span lightweight playgrounds to enterprise-grade evaluation platforms. They help teams version prompts, run controlled experiments, and observe LLM behavior in detail, which reduces errors and accelerates iteration. Adoption requires forethought about integration, governance, and long-term flexibility, but when aligned with existing workflows these tools materially improve reliability and time-to-production for LLM-powered products.