
Inbound Marketing: Complete Guide to Strategies, ROI, and Pricing in 2025
To save readers extensive research time, this article compiles verified data from official sources and trusted review platforms as of November 20, 2025.
What is Inbound Marketing?
Inbound marketing focuses on attracting customers through relevant and helpful content rather than interrupting them with traditional advertising. This customer-centric approach builds trust and establishes long-term relationships by providing value throughout the buyer’s journey.
Core Principles of Inbound Marketing
Inbound Marketing Flywheel: Attract → Convert → Close → Delight
| Stage | Primary Goal | What You Do | KPIs to Track |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attract | Bring qualified visitors | SEO, blog publishing, social distribution, topic clusters | Organic sessions, impressions, CTR, new users |
| Convert | Turn visitors into leads | Landing pages, lead magnets, forms, CTAs, webinars | Conversion rate, lead volume, CPL, form completion |
| Close | Convert leads to customers | Email nurturing, segmentation, lead scoring, sales handoff | MQL→SQL rate, win rate, CAC, pipeline created |
| Delight | Drive retention and referrals | Customer enablement, support content, feedback loops, community | Retention, NPS/CSAT, upsell rate, referral volume |
Tip: Track one primary KPI per stage to avoid “metric overload” and keep execution focused.
The foundation of inbound marketing rests on four essential principles that guide strategic decision-making:
- Attract: Draw in the right audience with valuable content and optimized search visibility.
- Convert: Turn visitors into leads using compelling offers and conversion-focused landing pages.
- Close: Nurture leads into customers through targeted emails and personalized engagement.
- Delight: Continue providing value to encourage referrals and brand advocacy.
These principles create a flywheel effect where satisfied customers help accelerate growth through positive word-of-mouth.
Key Components and Methodologies
Successful inbound marketing integrates multiple methodologies that work together cohesively:
- Content Creation: Blog posts, ebooks, whitepapers, and videos addressing customer needs.
- Search Engine Optimization: Technical and content optimization to increase organic visibility.
- Social Media Marketing: Strategic distribution and community engagement across platforms.
- Email Marketing: Automated and personalized communication sequences.
- Marketing Automation: Workflows that scale tailored customer experiences.
Inbound Marketing Strategies and Tactics
Content Marketing
Content marketing is central to inbound success. Organizations should develop informative, engaging, or inspirational content that aligns with customer goals.
- Blog Content: Consistent publishing with SEO-optimized articles for defined buyer personas.
- Premium Content: Gated resources such as ebooks and webinars used to capture leads.
- Video Marketing: Tutorials, demonstrations, and thought leadership content.
- Case Studies: Customer success stories showcasing measurable business outcomes.
SEO Optimization
SEO aims to increase organic search visibility and attract qualified traffic. This requires a combination of technical expertise and strategic content alignment.
- Keyword Research: Identifying high-intent terms aligned with buyer journey stages.
- On-Page Optimization: Improving titles, meta descriptions, and internal linking.
- Technical SEO: Enhancing site speed, mobile performance, and crawlability.
- Content Optimization: Creating comprehensive resources matching search intent.
Social Media Engagement
Social media extends content reach and strengthens audience relationships. Each platform benefits from tailored strategies.
- LinkedIn: Ideal for B2B thought leadership.
- Twitter: Effective for real-time industry engagement.
- Facebook: Useful for community building and targeted campaigns.
- Instagram: Supports visual storytelling and brand personality.
Lead Generation and Nurturing
Converting visitors into leads requires optimized conversion points and well-designed nurturing workflows.
- Landing Pages: Purpose-built pages for driving specific conversions.
- Lead Magnets: High-value resources offered in exchange for contact details.
- Email Sequences: Automated workflows guiding leads through the funnel.
- Progressive Profiling: Gradual data collection to improve personalization.
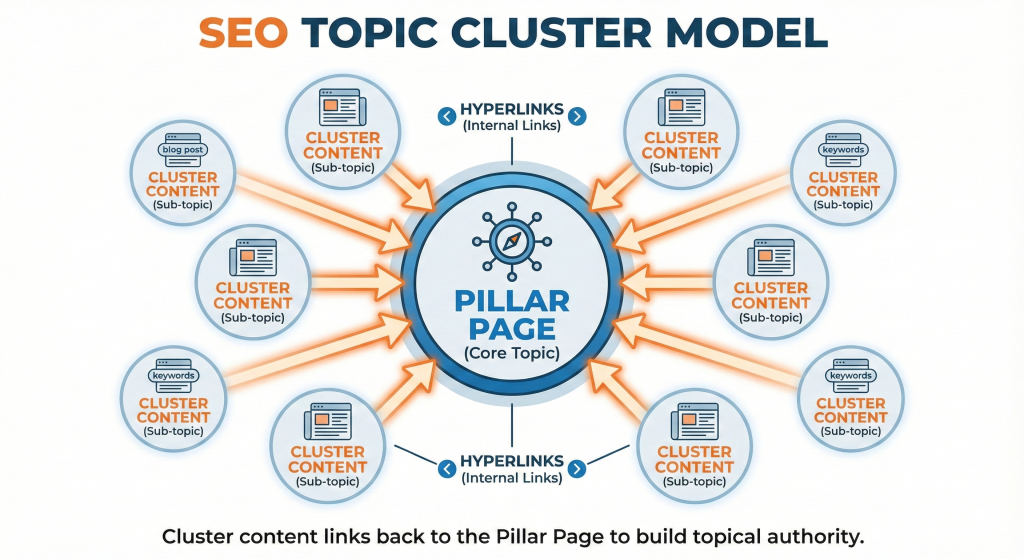
How I’d Execute It: The “Topic Cluster” Shortcut
Most people fail at Inbound Marketing because they write random blog posts. I don’t guess; I build Topic Clusters. This method forces Google to see you as an authority on day one.
Here is my exact 3-step execution plan:
1. Pick One “Pillar” Topic (Not a Keyword) Don’t start with “SEO tips.” Start with a broad, high-value problem your product solves, like “Remote Team Management.” This is your center of gravity.
2. Write the “Pillar Page” First Create a massive, 3,000-word guide covering every aspect of that topic. Do not gate this content. Give it away for free. This page serves as your traffic hub.
3. Create 5-10 “Cluster” Posts Write shorter, specific articles related to the Pillar (e.g., “Best Slack Integrations for Remote Teams”).
- Crucial Step: Link every single Cluster post back to the Pillar page using the exact anchor text.
- The Result: This internal linking structure signals to search engines that your Pillar page is the ultimate resource, boosting its ranking faster than isolated posts.
Measuring the ROI of Inbound Marketing
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Inbound ROI measurement requires tracking metrics across the customer lifecycle. These KPIs support effective optimization and budgeting.
- Traffic Metrics: Organic sessions, direct visits, and referral performance.
- Conversion Metrics: Lead capture rates, email subscriptions, and resource downloads.
- Engagement Metrics: Time on page, bounce rates, and social interactions.
- Revenue Metrics: Acquisition cost, lifetime value, and qualified lead generation.
Attribution Modeling
Attribution modeling clarifies which touchpoints influence conversions and revenue outcomes.
- First-Touch Attribution: Credits the initial interaction.
- Last-Touch Attribution: Credits the final action before conversion.
- Multi-Touch Attribution: Spreads credit across touchpoints.
- Time-Decay Attribution: Prioritizes touchpoints closer to conversion.
Tools for ROI Tracking
Modern analytics and automation tools support comprehensive inbound performance tracking.
- Google Analytics: Monitors traffic and conversions.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Enables lead scoring and campaign tracking.
- CRM Integration: Provides sales pipeline visibility.
- Social Media Analytics: Tracks platform-specific engagement.
Pricing and Subscription Models
Pricing Overview: Common Inbound Marketing Subscription Tiers
| Tier | Typical Monthly Cost Range | What’s Usually Included | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starter | ~$20–$100 | Basic email, simple automation, forms/landing pages, light reporting | Small teams starting inbound and capturing first leads |
| Professional | ~$400–$1,000 | Advanced automation, segmentation, A/B testing, stronger analytics | Growing teams optimizing conversion and pipeline impact |
| Enterprise | $1,250+ | Deeper reporting, complex workflows, permissions, integrations, support | Large orgs needing governance, customization, and scale |
Note: Your total inbound cost also includes content production and staffing—not just software subscriptions.
Cost Considerations for Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing budgets vary based on company size, industry, and goals. Key cost areas include technology, content, and personnel.
- Technology Stack: Automation tools, CRM platforms, and analytics software.
- Content Production: Writing, design, and video creation.
- Advertising Spend: Paid social and search promotion.
- Personnel Investment: Marketing and content specialists.
Pricing Models for Inbound Marketing Services
Organizations can build in-house capabilities or partner with agencies. Pricing varies by platform and service level.
HubSpot’s Marketing Hub starts at $20 per month for the Starter plan (source: https://www.hubspot.com/pricing/marketing), making it accessible for small businesses beginning their inbound journey.
Enterprise platforms like Salesforce Account Engagement (Pardot) start at approximately $1,250 per month, reflecting advanced automation and CRM integration capabilities.
- Starter Plans: Basic email and lead capture tools.
- Professional Plans: Enhanced automation, A/B testing, and analytics.
- Enterprise Solutions: Custom integrations, deeper reporting, and dedicated support.
Practical Insight: Why Inbound Marketing ROI Takes Time to Compound
One of the most common misconceptions about inbound marketing is expecting immediate ROI comparable to paid campaigns. In practice, inbound performance compounds over time because content, search visibility, and audience trust accumulate rather than reset each month.
Early-stage programs often show modest results, especially during the first three to six months. However, organizations that maintain consistent publishing, SEO optimization, and lead nurturing typically see accelerating returns as older assets continue generating traffic and qualified leads. This compounding effect explains why inbound marketing budgets are often underestimated when evaluated on short-term performance alone.
Understanding inbound as a long-term system rather than a campaign helps set realistic expectations and prevents premature strategy changes that limit overall impact.
Inbound Marketing vs. Outbound Marketing
Inbound vs. Outbound Marketing: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Aspect | Inbound Marketing | Outbound Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Core Approach | Attracts with helpful content and intent-based discovery | Pushes messages via ads, cold outreach, and interruptions |
| Customer Experience | Value-first, trust-building, educational | Attention-first, often time-sensitive or promotional |
| Cost Structure | Upfront content investment; compounding long-term returns | Ongoing spend required to maintain reach and impressions |
| Lead Quality | Often higher intent; self-qualified through content | Broader targeting; qualification happens later |
| Time to Results | Medium to long-term (compounds over time) | Short-term spikes (depends on spend and targeting) |
| Measurement | Multi-touch attribution across longer journeys | Often easier to track immediate responses and conversions |
| Best Use Case | Complex solutions, long sales cycles, relationship-driven growth | Launches, promotions, brand awareness, demand capture |
Practical approach: Use inbound to build compounding demand, and outbound to amplify your best-performing inbound assets.
A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the differences between inbound and outbound approaches helps organizations plan effective marketing strategies.
- Customer Experience: Inbound delivers value first; outbound relies on interruption-based messaging.
- Cost Structure: Inbound requires upfront content investment, while outbound depends on ongoing ad spend.
- Targeting Precision: Inbound attracts self-qualified leads; outbound targets broader audiences.
- Measurement Complexity: Inbound attribution spans longer timelines; outbound often yields immediate metrics.
When to Use Each Approach
Most organizations benefit from a hybrid strategy, combining the strengths of both inbound and outbound tactics to meet specific goals.
- Inbound Works Best: Long sales cycles, complex solutions, relationship-driven sales.
- Outbound Excels: Time-sensitive campaigns and brand awareness initiatives.
- Hybrid Approaches: Using outbound advertising to amplify inbound content.
The most effective marketing strategies balance inbound methodology with targeted outbound tactics to optimize performance and reach.

Editor’s Summary
Inbound marketing in 2025 functions less as a campaign tactic and more as a long-term growth framework built on trust, relevance, and measurable performance. As audiences become more selective and acquisition costs continue to rise, value-driven content and organic discovery have become central to sustainable demand generation.
This guide shows that successful inbound programs are not defined by individual tools or channels, but by how well content, SEO, automation, and analytics work together across the buyer journey. While pricing models and platforms vary widely, the core requirement remains consistent execution supported by clear KPIs and realistic ROI expectations.
When approached as a compounding system rather than a short-term initiative, inbound marketing enables organizations to build durable visibility, stronger customer relationships, and defensible growth over time.